Why you lose it
One of the reasons your body is so special is its ability to heal itself. Within your fascial tissueare cells that create fascial adhesions around an injury to provide extra stability and restrict painful movement while the damaged tissue is repaired. The restricted movement is just enough to facilitate the healing process while at the same time allowing you some freedom to move. In the ancient world where the human body was forged, this healing process took place over the course of a few days or weeks. Movement was a necessary and key factor in the healing process. Early man did not have the luxury to spend a few days in bed to fully recover. He had to move to survive, and so he had to heal while moving, which is why this process of building fascial adhesions is so special. Movement works in unison with the circulatory system as a secondary mechanical pump and flushes the injured tissue with fresh blood. This flush of blood flow removes waste by-products, brings in fresh nutrients and speeds up the healing process dramatically. As the injured area recovers, the body once again is able to utilize full, pain free, movement patterns that completely break down the fascial adhesions.
Today we have a problem: we no longer live in that ancient world. Our cultural landscape has dramatically changed our lifestyle over the past 100 years – especially in the last 20. Instead of hunting, gathering, and harvesting our food, utilizing our body in daily acts of survival, we spend most of our time sitting, in front of a computer or in a car. Compared to a mere couple hundred years ago, the lifestyle of even the most active person in any industrialized country today would be considered relatively sedentary.
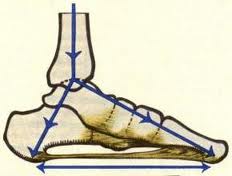
When you do not get adequate functional movement, you no longer put your mechanical pump to use. This slows down the healing process as restrictive adhesionsdo not get broken down. Instead, lack of movement communicates to your body that you are still injured and so it continues to build up even more adhesions to further stabilize and restrict motion around the supposedly injured areas. Over time, thesefascial adhesions become so thick and strong that you permanently lose your full range of motion and function. Examples are: losing the ability to fully turn your head in one or both directions to see behind yourself while walking or driving; the ability to raise your arms fully over your head while maintaining a stable spine and scapula; the ability to do a deep squat with your feet flat on the floor; the ability to walk, run or sprint without pain. Without enough functional movement your body assumes you are in a continual state of injury. Eventually this becomes a full-time reality. This is the primary reason that I find deep tissue massage therapy, such as myofascial release, to be so important. I can manually break down fascial adhesions and increase functional range of motion. I can prime the mechanical pump, facilitating waste product removal and nutrient delivery back into the tissue. In essence this removes years of fascial buildup and facilitates a speedy return to functional movement.
Not Just Any Movement, What you need is Functional Movement A sedentary lifestyle means we do not use our bodies the way a human body was designed to move. This has become the reality of our lives. On a daily basis, we fail to utilize the vast array of movement patterns that are possible. Plus the intensity of our movements has softened. All kinds of technologies have made our lives much easier in most regards. This means that we must go out of our way to move our body the way it must functionally move.
A sedentary lifestyle means we do not use our bodies the way a human body was designed to move. This has become the reality of our lives. On a daily basis, we fail to utilize the vast array of movement patterns that are possible. Plus the intensity of our movements has softened. All kinds of technologies have made our lives much easier in most regards. This means that we must go out of our way to move our body the way it must functionally move.
Functional movement training is vital. You cannot not get the movement your body needs to maintain pain-free health and vitality by sitting in front of a computer. You must move. I am not talking about the traditional types of exercises that are likely coming to your mind. I’m not talking about running for hours on end on pavement in a straight line. I’m not talking about lifting weights while sitting on a nice cushioned bench or using a machine. Your body needs functional movement. It needs to move the way it was designed to move. Running and traditional weight training are small portion of functional training and tend to be overly repetitious in very specific movement patterns. They do not utilize the postural stabilization and functional movement patterns your body craves. To your body not using a functional movement pattern is almost the same as not moving. And as I said earlier, if you don’t use it, you lose it. Even if you run or lift weights 7 days a week, if you do not lift your arm over your head, over time you will lose the ability to do so. Your body recognizes this as an injury and begins the healing process discussed above, but now to your detriment.
What is Functional Movement?
My definition is simple. You have a body for a reason. Functional movement is what happens when you use your body to meet all of its designed purposes: flexing, extending, pulling, pushing, rotating, changing directions, running, walking, jumping, sprinting and climbing. If you are designed to do it, then use your body to do it. If you don’t, you will eventually lose your ability to do it, which will lead to a higher risk ofchronic pain and injury in your life.
 As a personal trainer and deep tissue massage therapist, my entire focus is on functional movement – no exceptions. From the start we make sure you have pain free, functional range of motion with a stable posture. We make use of deep tissue massage, flexibility and corrective exercises (you can see examples of corrective exercises here, here and here) to open up your neck, chest, and shoulders so you can turn your neck to check your blind spot, or lift a box overhead without pain or injury. We increase flexibility in your hips so you can easily squat deeply without knee or back pain. We get you to walk and run comfortably again – no more dread of a painful trip up the stairs, to the mailbox, or to the car.
As a personal trainer and deep tissue massage therapist, my entire focus is on functional movement – no exceptions. From the start we make sure you have pain free, functional range of motion with a stable posture. We make use of deep tissue massage, flexibility and corrective exercises (you can see examples of corrective exercises here, here and here) to open up your neck, chest, and shoulders so you can turn your neck to check your blind spot, or lift a box overhead without pain or injury. We increase flexibility in your hips so you can easily squat deeply without knee or back pain. We get you to walk and run comfortably again – no more dread of a painful trip up the stairs, to the mailbox, or to the car.
Once your functional range of motion and postural stability are improved you get to start having some real fun. In these workouts you fine tune this high performance machine that is your body by working it to meet all of its designed purposes. You will sweat, burn calories, build muscle, get stronger, move better, have more energy, become more capable and productive in your life, look better, reduce body fat, reduce stress, pain and injury, and most importantly: you will feel better in your body.